Using IMS Recovery Expert v2.1 to simplify, improve, and automate backup and recovery
29 August, 2010A new class of storage-aware data management tools is evolving that integrates FlashCopy fast-replication facilities with database management systems to provide fast and non-intrusive database system-level backup and cloning solutions. Storage-aware data management tools like IBM IMS Recovery Expert for z/OS V2.1 and Db2 Recovery Expert for z/OS help simplify backup, recovery, and disaster recovery strategies by using automation to coordinate database system operations with FlashCopy and other storage-based fast-replication facilities. Data copy processes are offloaded and performed efficiently in the storage processors, which saves host CPU and I/O resources.
Storage-aware data management tools provide facilities to link and coordinate application and data management organizations with business continuity and storage administrators. By using the FlashCopy facilities to perform traditional data copy functions, you can implement new backup and recovery methods and simplify business continuity operations by transforming tedious disaster recovery processes into efficient disaster restart procedures. Figure 1 shows how storage-aware backup and recovery solutions can be used to integrate application and database administration domains with business continuity and storage administration domains.
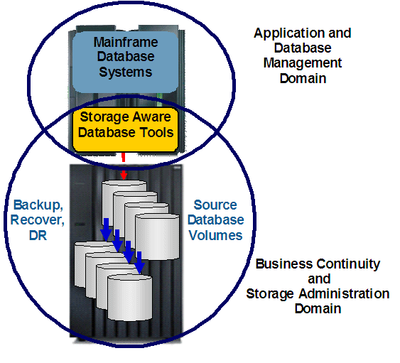
Figure 1 Storage-aware database backup and recovery solutions
ims recovery expert v2.1 is storage-aware
IMS system-level backup (SLB) methodologies have been used by some organizations for many years as an efficient and effective way to back up IMS systems. System-level backups have been created by storage organizations using full volume dumps and storage-based fast replication facilities. The backups are shipped offsite where they are used to provide the foundation for traditional IBM IMS® disaster recovery procedures. These storage-based backups tend not to be used by DBAs (database administrators) to perform local or disaster recovery operations because it is difficult to coordinate the data restoration from volume backups with database recovery processes without supporting automation. The complexity associated with using volume backups and the familiarity of using IMS and host-based copy methods has guided IMS DBAs to use traditional image copy backups for local site recovery and for disaster recovery purposes.
IMS Recovery Expert V2.1 is a storage-aware backup and recovery tool that resolves FlashCopy organizational and technology usage conflicts by allowing FlashCopy facilities to be exposed to IMS DBAs in a transparent manner. IMS Recovery Expert V2.1 integrates FlashCopy facilities to automate and simplify backup and recovery processes. IMS system-level backup methods are the foundation for these backup and recovery processes. IMS system-level backups performed using FlashCopy have many operational advantages.
- Backup, recovery, and disaster recovery procedures are simplified and backup processing and administration costs are reduced.
- Application availability is increased because IMS systems can be backed up instantaneously without affecting running applications. Backup windows are eliminated and application processing windows can be extended.
- Processing costs are reduced because backups are performed in the storage processor without using host CPU or I/O resources.
- You can coordinate FlashCopy operations with IMS activities to back up IMS systems. Backups can be validated at backup time to ensure all database resources are contained within the volumes being backed up.
- IMS system-level backups can be used for multiple backup purposes and save storage resources. IMS system-level backups can support local system recovery, application recovery, database recovery, as well as provide offsite disaster restart support for IMS systems.
- Automated system-level backup offload facilities can archive disk-based backups to tape. You can use the tape archive copies for subsequent local data recovery or for offsite disaster restart and recovery purposes.
- Data consistency is ensured during the backup process. Data consistency can be maintained across volumes by using IMS RE V2.1 suspend operations. Storage-based consistency functions can also be used to maintain data consistency during the backup process.
- System-level backups reduce recovery time. IMS systems or application databases are restored instantaneously from a system-level backup using FlashCopy facilities while IMS recovery operations are performed in parallel to the restoration process to minimize recovery time and reduce application down time.
- IMS system-level backups provide an effective disaster restart business continuity solution that simplifies disaster recovery operations. Disaster recovery becomes as simple as restarting from a power failure.
ims storage-aware backup and recover process flow
Storage-aware IMS system-level backup solutions use volume-based FlashCopy operations to back up IMS systems. Volume-level backups have many operational advantages over data-set copy methods. Volume-based FlashCopy speed up the IMS backup processes because it is executed quickly, can leverage storage-based consistency functions, and uses storage processor resources efficiently.
When the IMS system volumes are discovered and backup target volumes are associated, FlashCopy facilities are used to back up the IMS system instantaneously without affecting running applications. Backup volume and associated database recovery information is stored in a metadata repository and used during recovery and backup offload processing. Figure 2-A shows IMS RE V2.1 using volume-based FlashCopy to create a system-level backup for IMS.
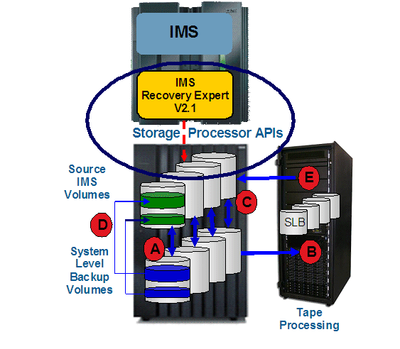
Figure 2 IMS storage-aware database backup and recovery
A - IMS system-level backup created by using volume-based FlashCopy
B - Disk-based system-level backup offloaded to tape
C - Disk-based system-level backup used to restore an IMS system
D - IMS application, or database recovery from a system-level backup
E - Restoring an IMS system or database from an offloaded system-level backup
IMS system-level backups on disk provide fast and effective restore and recovery operations. However, maintaining multiple backup generations on disk can be cost-prohibitive. IMS RE V2.1 has tape offload facilities to provide for long-term backup retention while allowing recovery to be performed from the archived copy. Figure 2-B depicts an IMS system-level backup that is archived to tape by IMS RE V2.1. The archived copy can be used for subsequent IMS system, application, and database recovery.
IMS system-level backups are restored from disk or tape automatically when recovery operations are required. The recovery process determines the optimal backup to restore that provides the most expeditious recovery. The recovery process determines whether to restore a disk-based IMS system-level backup or whether to restore an IMS system-level backup that has been archived to tape based on recovery scope and which restoration method provides the fastest recovery.
When recovering IMS systems by using a system-level backup that is on disk, the FlashCopy facilities are used to restore the data at a volume level to expedite the restoration process. IMS system recovery processes are performed in parallel while the data volumes are being restored. Database logs are used to roll forward the restored application data. Figure 2-C depicts an IMS system recovery operation where volume-based fast replication is used to restore database data. Figure 2-E depicts an IMS system recovery from an IMS SLB that has been archived to tape.
When IMS applications or databases are recovered, appropriate corresponding data sets are restored from the system-level backup volumes by using data set FlashCopy facilities. Application recovery time is reduced because the data restoration process performed in the storage processor is done in parallel with the IMS recovery processes. That is, IMS logs are applied while data is being restored in the storage processor as a result of the data set FlashCopy operation. The parallel restore and recovery processing shortens overall recovery time and reduces application downtime during the recovery process. Figure 2-D depicts an IMS application or database recovery operation where data-set level fast replication is used to restore database data.
intelligent recovery manager
IMS RE V2.1 has an embedded Intelligent Recovery Manager that coordinates and manages data restoration, recovery, and post recovery processes. The Intelligent Recovery Manager determines the SLB or image copy that provides the most expedient recovery. If an SLB is chosen for data restoration, IMS RE V2.1 drives appropriate FlashCopy facilities to restore the data. Recovery and post recovery products and utilities can be configured and used to perform your recovery and post recovery processing needs. Figure 3 provides an overview of IMS RE V2.1 Intelligent Recovery Manager and processes it manages.
When IMS recovery is needed, the IMS Intelligent Recovery Manager analyzes all available recovery assets and uses the configured recovery utilities to drive the steps needed to recover an IMS system, application, or database in the most efficient manor. All recovery jobs are setup through an ISPF interface and all recovery utilities can be managed from a centralized point. Complex IMS recover processes are simplified, recovery steps are automated and recovery time is reduced.
IMS RE V2.1 promotes parallel recovery operations by restoring backup copies while IMS recovery operations are performed in parallel. The Intelligent Recovery Manager invokes appropriate FlashCopy facilities and initiates IMS recovery procedures while data is being restored in the storage processor. Parallelizing the data restoration and IMS recovery processes shortens recovery time and reduces IMS recovery time objectives.

Figure 3 IMS RE V2.1 Intelligent Recovery Manager
ims disaster restart and recovery
An IMS system-level backup simplifies disaster recovery operations and reduces recovery time objectives. IMS system-level backups can be used to restart the IMS system at a point in time when the backup was performed. IMS system-level backups can also be rolled forward using available database logs and recovery assets at your disaster recovery site.
An IMS system-level backup is a "restartable" copy. A restartable IMS backup copy has a dependent-write consistent data state from an I/O perspective. This data state is identical to that created by a power failure. A restartable IMS copy can be created by invoking IMS or storage-processor data consistency functions when an IMS system-level backup is created. For example, a restartable IMS copy can be created by suspending IMS using the IMS RE V2.1 suspend feature or by using a storage-based consistency function while FlashCopy commands are executed to create a system-level backup.
IMS disaster recovery operations that use a system-level backup as input can use traditional IMS emergency restart procedures at a disaster recovery site to recover their IMS systems. IMS recovery is performed implicitly using IMS emergency restart procedures to transform the dependent-write consistent data state into a transactionally consistent data state. IMS disaster recovery procedures can become as simple as restarting IMS system from a power failure.
IMS RE V2.1 includes an Intelligent IMS Disaster Recovery Manager which has local and remote DR site components. The local component tracks IMS log archive processes and correlates them to IMS SLB creation and offsite transport. The remote DR site component provides facilities to roll the offsite IMS SLB forward using image copies, change accumulations, and archive logs that have been subsequently sent to the DR site. Thus, tedious IMS disaster recovery operations can be transformed into efficient disaster restart procedures to simplify the IMS recovery process, reduce recovery time objectives, and reduce recovery point objectives at the disaster recovery site.
Offloading FlashCopy-based IMS system-level backups to tape and then transporting the tapes to a disaster recovery site provides the foundation for a tape-based disaster restart solution. Tape-based disaster restart solutions simplify disaster recovery operations, reduce recovery time objectives, and provide similar advantages to storage-based business continuity solutions that use remote storage replication such as IBM PPRC (peer-to-peer remote copy). Tape-based disaster restart solutions can provide an excellent and cost-effective tertiary disaster recovery solution when implemented with PPRC Metro Mirror remote mirroring solutions.
conclusion
IMS backup, recovery, and disaster recovery operations can be simplified and improved by leveraging your storage system fast-replication facilities through storage-aware IMS management tools. IMS RE V2.1 integrates FlashCopy fast-replication facilities with IMS systems to enable high availability though improved backup, recovery and disaster recovery procedures. By using IMS RE V2.1, DBAs can use FlashCopy fast-replication facilities safely and transparently while simplifying IMS administrative processes and reducing CPU and I/O utilization.
about the author
Ron Haupert is a Senior Technologist with Rocket Software and is a database professional with over 30 years of related experience. He specializes in federated database interoperability and management, high availability, backup / recovery, business continuity, and storage system integration.
about Rocket Software
Rocket Software (www.rocketsoftware.com) is a global software development firm that builds enterprise products and delivers enterprise solutions in the following segments: Business Intelligence and Analytics; Storage, Networks, and Compliance; Application Development, Integration, and Modernization; and Database Servers and Tools. Rocket is engaged in business and technology partnerships with IBM, EMC, Fujitsu, HP Enterprise Services, Hitachi Data Systems, Avaya, Motorola, Epicor, and many others. The company is headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts, USA.
Recommended For You
Rocket Software Unveils Innovations to Scale IT Impact Through Resilience, Automation, and AI-Powered Agility
New capabilities improve developer workflows, streamline operations, and fortify IT systems without added complexity
Rocket Software Celebrates 35 Years of Innovation in IT Modernization
From Start-up to Global Leader, Rocket Software Celebrates Decades of Innovation and Prepares for the Future
Rocket Software Transforms Hybrid Cloud Data Integration with Rocket® DataEdge™
Comprehensive software suite enables end-to-end discovery, integration, and management of mainframe, distributed, and cloud data to advance AI and analytics initiatives